Have you considered how something as seemingly benign as inflammation could be influencing obesity rates? The intricate relationship between these two factors offers profound insights into our health journey.
What You Will Learn
- Chronic inflammation can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Understanding the dual nature of inflammation—acute versus chronic—provides essential context for obesity management.
- Dietary choices, such as the consumption of processed foods, significantly impact inflammation levels.
- The role of immune cells in adipose tissue is crucial for understanding inflammation's impact on obesity.
- Future research focusing on anti-inflammatory treatments may enhance obesity management strategies.
Understanding Inflammation's Role in Obesity
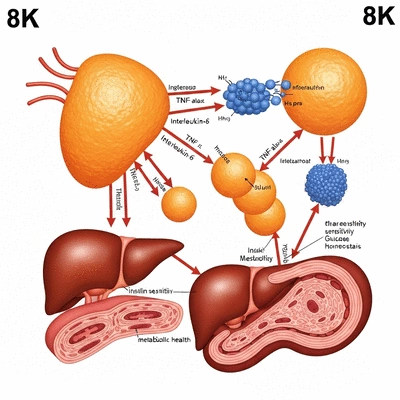
This visual outlines the distinct characteristics of acute vs. chronic inflammation and their specific connections to obesity, highlighting how each type impacts metabolic health.
Understanding the Connection Between Inflammation and Obesity
When we think about obesity, we often consider factors like diet and exercise. However, there's a deeper layer to this issue: inflammation. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury and infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can significantly impact our health. So, how does this relate to obesity? Chronic inflammation can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to weight gain and making it harder to lose weight. This connection is crucial for us to understand as we navigate the complexities of obesity.
I often tell my clients that recognizing inflammation as a player in obesity management is a game-changer. By understanding how it works, we can take meaningful actions to address it. This means looking beyond the scale and focusing on our body's internal environment. So, let’s dive deeper into what inflammation really is and how it relates to obesity.
What is Inflammation and How Does it Relate to Obesity?
Inflammation can be categorized into two types: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is a short-term response, like redness and swelling after an injury. In contrast, chronic inflammation lingers over time and can arise from various factors, including obesity. When fat cells become enlarged and dysfunctional, they can release inflammatory substances that harm the body. This not only contributes to further weight gain but also increases the risk of diseases like diabetes.
- Acute inflammation is temporary and often beneficial.
- Chronic inflammation is prolonged and can lead to health issues.
- Obesity often induces a state of chronic inflammation in the body.
Understanding this relationship is crucial. When we effectively manage inflammation, we can pave the way for better health outcomes. It’s a reminder that our journey towards a healthier lifestyle isn’t just about losing weight; it’s about cultivating an environment within our bodies that promotes healing and balance.
The Rising Impact of Chronic Inflammation in Modern Health
In today's world, factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and increased stress are contributing to a rise in chronic inflammation. This is particularly concerning as it correlates with the obesity epidemic. When we think about our habits—like choosing processed foods over whole foods—every choice matters. I often encourage my readers to reflect on what they consume and how it could influence their health.
- Processed foods can increase inflammation.
- Stress management is vital for reducing chronic inflammation.
- Regular physical activity helps mitigate inflammatory responses.
As we explore these connections, it's essential to consider how adopting healthier habits can not only help us manage obesity but also reduce inflammation. This holistic approach aligns perfectly with our mission at What Is Obesity, where we aim to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to make impactful changes.
The Role of Immune Cells in Obesity Development
Now that we’ve established the link between inflammation and obesity, let’s discuss the role of immune cells in this process. It’s fascinating to realize that our immune system plays a pivotal role in managing body weight. When we delve into these details, we uncover how immune cells interact with adipose tissue, which is crucial for understanding obesity better. Research indicates that immune cells in adipose tissue contribute significantly to chronic inflammation, influencing the development of obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Pro Tip
Did you know? Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can significantly reduce chronic inflammation and support weight management. Consider adding more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like those found in olive oil and fatty fish. These foods not only help combat inflammation but also promote overall metabolic health!
Frequently Asked Questions About Inflammation and Obesity
- 1. How does chronic inflammation contribute to weight gain?
- Chronic inflammation disrupts metabolic processes, particularly insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance. This makes it harder for the body to use glucose effectively, promoting fat storage and making weight loss more challenging.
- 2. What is the difference between acute and chronic inflammation?
- Acute inflammation is a short-term, localized response to injury or infection, often beneficial for healing. Chronic inflammation, however, is a prolonged, systemic response that can arise from factors like obesity and contributes to various health issues over time.
- 3. Can diet impact inflammation levels in the body?
- Yes, dietary choices significantly influence inflammation. Consuming processed foods, high sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase inflammation, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce it.
- 4. What role do immune cells play in obesity?
- Immune cells, particularly those found in adipose (fat) tissue, contribute to the inflammatory environment in obese individuals. Dysfunctional fat cells release inflammatory substances, and immune cells respond, perpetuating a cycle of inflammation that impacts metabolism and further weight gain.
- 5. What are some future directions for treating obesity by targeting inflammation?
- Future treatments for obesity may involve dietary interventions tailored to reduce inflammation, as well as therapeutics specifically designed to target inflammatory pathways in adipose tissue. These approaches aim to improve metabolic outcomes by addressing the root cause of inflammation.
Summarizing the Role of Inflammation in Obesity Development
As we delve into the intricate relationship between inflammation and obesity, it becomes clear that inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of obesity-related health issues. The evidence is compelling: chronic inflammation can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to insulin resistance and various metabolic disorders. By understanding this connection, we can better address the challenges faced by those struggling with obesity.
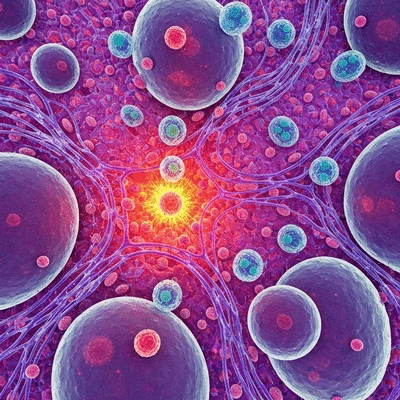
Key insights about inflammation include its influence on immune cells, the various cytokines involved, and how different types of fat tissue respond to these inflammatory signals. In particular, it's important to recognize that the immune system is not merely a defender against pathogens; it also plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and energy balance. This realization opens a pathway for innovative approaches to obesity management.
Key Takeaways on Immune Contributions to Metabolic Health
- Chronic inflammation is a significant factor that exacerbates obesity and related metabolic conditions.
- Immune cells, particularly those in adipose tissue, can drive or mitigate inflammation based on their state and activity.
- Understanding the roles of various cytokines can lead to targeted treatments that might reduce inflammation and improve metabolic health.
- Different fat depots (visceral vs. subcutaneous) have distinct inflammatory profiles, influencing overall health.
- Future research is essential to uncover the complexities of inflammation in obesity and how we can leverage this knowledge in treatment.
As we can see, the interplay between the immune system and metabolic health is complex but essential. Each of these points highlights a crucial aspect of how inflammation contributes to the development of obesity and its associated disorders. By focusing on these areas, we can pave the way for more effective interventions that are not only science-based but also practical for individuals looking to improve their health.
Future Directions for Research and Treatment Innovations
The future of obesity treatment may very well hinge on our ability to address inflammation effectively. Researchers are exploring a variety of approaches that could reshape how we think about obesity management. For instance, investigating the role of dietary interventions in moderating inflammation presents exciting possibilities. Tailoring nutrition to reduce inflammation could enhance metabolic health significantly.
Moreover, ongoing studies into therapeutics targeting inflammatory pathways may revolutionize treatment options. We may soon have access to medications that can specifically reduce inflammatory responses in adipose tissue, thereby improving metabolic outcomes. These developments will require collaboration among health professionals, researchers, and patients to ensure that innovations are effective and accessible.
Engaging with the Content: What’s Next?
Resources for Further Reading on Inflammation and Obesity
For those eager to learn more about the intricate link between inflammation and obesity, we have curated a selection of resources that can deepen your understanding:
- Understanding Inflammation and Its Role in Obesity
- How Inflammation Affects Weight Management
- Obesity Action Coalition: Inflammation Insights
These readings will provide a solid foundation and help you navigate the complexities of obesity and inflammation. Remember, knowledge is a powerful tool in fostering healthier lifestyles!
Join the Conversation: Share Your Thoughts and Experiences
I invite you to engage with our community at What Is Obesity. Your personal experiences and insights matter! Sharing your journey with obesity, whether through struggles or triumphs, can inspire others and foster a supportive environment. Have you noticed the effects of inflammation on your health? Let's discuss! Feel free to leave your thoughts in the comments section or reach out through our social media channels.
Together, we can continue to explore this crucial topic and work towards a healthier future. What do you think is the key to tackling obesity? Let's take this journey together!
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to obesity and can disrupt metabolic processes.
- Understanding the types of inflammation—acute versus chronic—helps in managing obesity effectively.
- Diet and lifestyle choices, such as reducing processed foods and managing stress, play a crucial role in inflammation levels.
- Immune cells in adipose tissue can either drive or mitigate inflammation, influencing weight management.
- Future obesity treatments may focus on dietary interventions and therapeutics targeting inflammatory pathways.