What if the number on the scale isn't the whole story? When it comes to obesity, understanding the nuances surrounding this complex condition is key to effective management and improved health outcomes.
What You Will Learn
- Obesity is a chronic disease influenced by metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial factors, making it essential to consider health beyond just BMI.
- Adipose tissue plays a crucial role in hormone regulation and energy balance; its dysfunction can lead to significant health complications, including insulin resistance.
- Metabolic syndrome, characterized by insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol, is closely linked to obesity and increases the risk of serious health issues.
- Recognizing comorbidities like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers can motivate individuals to make lifestyle changes that improve overall health.
- The economic impact of obesity affects healthcare costs and workplace productivity, highlighting the importance of addressing this public health crisis effectively.
- Self-management strategies such as setting realistic goals, utilizing telehealth services, and joining community programs can empower individuals on their weight control journey.
Understanding the Multifaceted Nature of Obesity
Obesity is a complex condition influenced by metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial factors. The visual below highlights key aspects and associated health risks, emphasizing that it's more than just a BMI reading.
Obesity Beyond BMI: A Multifaceted Condition
"It's not just about losing weight; it’s about improving overall health and quality of life!"
Health & Economic Impact of Obesity
"Understanding these risks is crucial for motivating lifestyle changes."
Self-Management & Support Strategies
"It’s essential to remember that you’re not alone in this journey!"
Understanding Obesity as a Chronic Disease
When we think about obesity, it's essential to recognize that its definition goes far beyond a simple number on the scale or a body mass index (BMI) calculation. Obesity emerges as a complex condition that intertwines various factors including metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial dimensions. The World Health Organization emphasizes that obesity and overweight are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. As someone deeply invested in this field, I can affirm that understanding these complexities is crucial for addressing the obesity epidemic effectively!
For instance, many individuals may fall into the BMI category classified as "overweight" or "obese," yet their metabolic health can vary dramatically. Some may have healthy metabolic profiles despite a higher BMI, while others with a normal weight may struggle with metabolic dysfunction. This nuanced view sheds light on why a one-size-fits-all approach is inadequate in managing obesity.
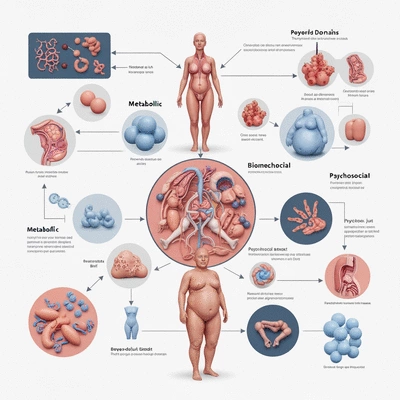
What Defines Obesity Beyond BMI?
- Metabolic health: This refers to how well your body can process food and manage energy.
- Biomechanical factors: Excess weight can affect joint health, mobility, and overall physical function.
- Psycho-social dimensions: Emotional and social factors often play powerful roles in how individuals experience and manage obesity.
Recognizing these dimensions is vital in developing effective strategies for obesity management. It's not just about losing weight; it’s about improving overall health and quality of life!
The Role of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction
Adipose tissue, or body fat, is often perceived negatively, but it serves essential functions. When functioning correctly, it helps regulate hormones and energy balance. However, in cases of excess fat, it can lead to dysfunction that disrupts the body's normal processes, creating a spiral of health issues. This dysfunction is often linked to complications like metabolic disease and organ dysfunction. Research highlights that adipose tissue dysfunction is a crucial factor in the development of obesity-related complications.
For example, when adipose tissue becomes dysfunctional, it can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Additionally, excess fat can impact organ function, leading to complications such as fatty liver disease or cardiovascular issues. It's a stark reminder that managing obesity is about correcting these underlying issues, not just focusing on weight loss.
Understanding Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance
The connection between obesity and metabolic syndrome is profound, with insulin resistance serving as a critical link. Metabolic syndrome is characterized by a cluster of conditions—such as high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, and abnormal cholesterol—that increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
As we delve into this topic, it's essential to highlight that obesity can often lead to insulin resistance. This condition occurs when the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, making it challenging to regulate blood sugar levels. Understanding this relationship is key to developing effective management strategies and improving health outcomes for those affected by obesity.
The Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Now that we've established a foundation for understanding obesity, let's explore the implications it carries for overall health. The health risks associated with obesity are extensive and can significantly affect one's quality of life.
Comorbidities Linked to Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes: This condition is often a direct result of insulin resistance, which is common in individuals with obesity.
- Heart disease: Obesity increases the risk of various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension and heart attacks.
- Cancer: Studies have shown a link between obesity and an elevated risk of several types of cancer.
- Joint problems: The extra weight can put added stress on joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
As I often tell my patients, understanding these risks is crucial for motivating lifestyle changes. Recognizing that obesity is associated with numerous serious health conditions can help individuals take proactive steps toward better health!

The Economic Impact of Obesity on Public Health
We cannot overlook the broader implications of obesity, including its economic impact on public health systems. Rising obesity rates contribute to escalating healthcare costs and increased resource utilization. Studies have shown the significant economic burden of obesity, affecting healthcare expenditures and productivity. Acknowledging this reality is essential for informing public health policies and interventions!
Consider the following economic factors related to obesity:
- Healthcare costs: Treating obesity-related conditions accounts for a significant portion of healthcare spending.
- Workplace productivity: Obesity can lead to increased absenteeism and reduced work performance.
- Social services: Communities may need to invest more in health promotion and preventative services to address the obesity crisis.
Understanding the economic burden of obesity can galvanize action at both individual and societal levels. It's clear that we need collective efforts to tackle this issue comprehensively!
We Want to Hear From You!
As we explore the multifaceted nature of obesity, we want to know your thoughts! What challenges have you faced in managing obesity, and what strategies have worked for you? Share your experiences below:
Living with Obesity: Patient Perspectives and Stories
Living with obesity is not just about numbers on a scale; it’s a journey filled with challenges, triumphs, and often, profound resilience. Many individuals face daily struggles while managing their weight, but there are inspiring stories that remind us of the strength found in community support and personal determination. At What Is Obesity, we believe in sharing these narratives to empower others on similar paths.
Take, for instance, the story of Sarah, who found herself overwhelmed by the stigma surrounding obesity. Instead of letting it define her, she sought out community programs and online groups. These connections not only provided her with valuable resources but also fostered a sense of belonging. Have you ever felt the power of shared experiences? It can be truly transformative!
Self-Management Strategies for Long-Term Weight Control
Managing obesity effectively often requires robust self-management strategies. Here are some effective approaches that individuals can adopt:
- Telehealth Services: Accessing virtual consultations enables you to connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of your home.
- Community Programs: Joining local support groups can provide motivation and accountability, helping you stay on track.
- Goal Setting: Establishing realistic short-term and long-term goals can guide your journey, making progress more tangible.
- Mindfulness Practices: Incorporating mindfulness can enhance your relationship with food and exercise, reducing emotional eating triggers.
These strategies not only promote accountability but also create a supportive network. It’s essential to remember that you’re not alone in this journey! Many people are learning to navigate similar challenges, and sharing strategies can lead to remarkable insights and progress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: Is obesity solely determined by Body Mass Index (BMI)?
- A: No, obesity is a complex condition influenced by metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial factors, not just BMI. Metabolic health can vary significantly among individuals with similar BMIs.
- Q: What is adipose tissue dysfunction, and how does it relate to obesity?
- A: Adipose tissue dysfunction occurs when excess body fat disrupts normal bodily processes, leading to issues like insulin resistance, impaired organ function, and metabolic disease.
- Q: What is metabolic syndrome, and why is it linked to obesity?
- A: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions (high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol) that increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes. It is often linked to obesity through insulin resistance.
- Q: What are some major health risks associated with obesity?
- A: Obesity is linked to several comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, certain cancers, and joint problems.
- Q: How does obesity impact society economically?
- A: Obesity contributes to high healthcare costs, reduced workplace productivity due to increased absenteeism and decreased performance, and a greater need for social services.
- Q: What self-management strategies can help with long-term weight control?
- A: Effective strategies include utilizing telehealth services, joining community programs, setting realistic goals, and practicing mindfulness to manage emotional eating triggers.
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Obesity is a complex chronic disease: It involves metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial factors beyond just BMI.
- Importance of metabolic health: Metabolic profiles can vary greatly among individuals with similar BMI, highlighting the need for personalized management strategies.
- Adipose tissue dysfunction: Excess fat can disrupt normal body processes and lead to serious health complications, emphasizing the need to address underlying issues.
- Comorbidities: Obesity is linked to various health risks, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
- Economic impact: The rising rates of obesity contribute to increased healthcare costs and reduced workplace productivity.
- Effective self-management strategies: Utilizing telehealth, community programs, goal setting, and mindfulness can enhance long-term weight control.










